Solar energy is at the forefront of California’s efforts to reduce carbon emissions and achieve sustainability goals. Before installing a solar energy system, whether residential or commercial, it’s essential to navigate the permitting process. Permits are required to ensure that solar installations comply with local safety standards, building codes, and zoning regulations. California has made significant strides in encouraging solar adoption, but due to the complexity of various installation scenarios, the permitting process ensures that each system is safe, secure, and energy-efficient. The state’s commitment to renewable energy has led to a more streamlined and accessible permitting process in many regions, although requirements can vary from city to city or county to county. A successful solar installation not only meets the expectations of homeowners and businesses but also aligns with state and local safety standards. The permitting process is key to ensuring that the energy system operates safely and effectively.
Types of Solar Permits in California
When installing a solar energy system in California, multiple permits may be required depending on the nature of the project. Building permits are needed to ensure that the structure of the building can safely support the solar panels. This is especially important for roof-mounted systems, as the weight and installation methods must be assessed for safety. Electrical permits ensure that the solar system’s electrical components are properly installed and comply with National Electrical Code (NEC) standards. Zoning permits may be required in some cases, particularly for larger installations or those that might affect the aesthetic or structural integrity of the community. Fire safety permits are becoming increasingly common, particularly in areas prone to wildfires, to ensure solar panels are installed in compliance with fire safety codes. In certain cases, encroachment permits may be needed if the installation impacts public property or infrastructure. Each type of permit serves a distinct function in protecting public safety and ensuring compliance with state and local laws.
Current Laws and Regulations
California has a well-established framework of laws and regulations that govern the installation of solar energy systems. Key regulations include the California Building Standards Code (Title 24), which includes specific rules for residential and commercial solar installations, such as structural requirements, electrical safety, and energy efficiency. California’s Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) oversees the Net Energy Metering (NEM) program, which allows homeowners and businesses to receive credits for surplus solar energy sent back to the grid. Other regulations set by the California Energy Commission (CEC) address renewable energy targets and energy efficiency goals, which are often factored into the permitting process. For example, AB 2188 (2022) streamlined permitting for small-scale solar systems, aiming to cut through red tape for simpler residential installations. Local governments also impose additional rules that might affect solar projects, such as height limitations or special building codes, so understanding the specific regulations in your area is critical for ensuring compliance and avoiding delays.
Permit Process for Solar Installation
The process of securing a permit for a solar energy system installation involves several key steps. First, the installer must evaluate the property to determine if it’s suitable for solar panels, checking for roof orientation, angle, and the structural integrity of the home. Afterward, the installer prepares a set of plans, which include structural drawings, electrical diagrams, and a proposed system design. These plans are submitted to the local building department or jurisdiction for review. The department checks the plans against local building codes, electrical codes, and other regulations. In some cities, an expedited review process may be available for residential solar systems, making approval faster. If the application passes review, the local authority issues a permit, and installation can begin. After installation, a final inspection is required to ensure compliance with all local codes. If the installation is approved during the inspection, the system is granted permission to connect to the grid and begin operation.
Timeline for Solar Permitting
The timeline for obtaining solar permits in California varies based on factors like the size of the installation, the complexity of the project, and the jurisdiction. In general, the permitting process can take anywhere from one to eight weeks for residential solar systems. Smaller systems tend to face shorter timelines due to their simplicity, while larger or more complex projects can require more time for review and approval. Cities that have adopted streamlined permitting processes may approve applications more quickly, with some jurisdictions offering expedited reviews for smaller residential systems. However, local building department backlogs can significantly delay the approval process. A project involving new construction or significant structural modifications may also face additional delays due to the need for more extensive documentation or approvals. Additionally, once the permit is granted, installation and inspection may take additional time. Understanding the timeline and starting the process early can help homeowners avoid delays in getting their solar system up and running.
Local vs State Permitting
California has a combination of state-wide regulations and local ordinances that govern the solar permitting process. State laws, such as the California Solar Mandate, require all new residential buildings to include solar panels, and they set baseline requirements for safety and energy efficiency. However, individual cities and counties also have their own building codes, zoning laws, and additional requirements that may impact solar projects. For example, local authorities may impose height restrictions, aesthetic guidelines, or specific fire safety regulations, especially in high-risk areas like those prone to wildfires. While state law encourages solar adoption, it is the local jurisdictions that review and approve the permits for specific projects. It is important to understand the local permitting rules before starting the project to ensure compliance. Some cities may offer expedited permitting for small residential systems, while others may have more restrictive requirements. Navigating both state and local regulations is essential to a successful solar installation.
Documents Required for a Solar Permit in California
When applying for a solar permit in California, the following documents are generally required to ensure compliance with local building codes, safety standards, and energy regulations. These documents help local authorities assess the installation plans and ensure that the solar system is safe and efficient:
- Completed Permit Application Form
This form includes essential information about the property, the proposed solar installation, and the property owner. It may be submitted online or in person, depending on the jurisdiction. - Site Plan
A detailed map of the property showing the location of the solar panels on the roof or ground. It should include roof dimensions, placement of panels, and any obstructions such as chimneys, vents, or trees that might affect the installation. - Roof Plan
A roof diagram that includes the dimensions of the roof and the proposed locations for the solar panels. This helps inspectors verify that the roof is suitable for the solar installation. - Electrical Plans
A schematic of the electrical system, detailing how the solar panels will be connected to the building’s electrical grid. The electrical plan should include the inverter location, wiring layout, and any circuit protection devices, such as breakers. - Structural Engineering Report
A report from a licensed engineer confirming that the roof can support the weight of the solar panels and the mounting system. This is especially important for older or non-standard buildings. - Manufacturer Specifications
Documentation from the manufacturer of the solar panels, inverters, and other system components. This includes technical specifications such as the model, performance data, and warranty information for each component. - Energy Compliance Forms
Forms that demonstrate the system meets California’s energy efficiency standards, including Title 24 requirements. These forms are often completed by a contractor or energy consultant and show that the system will meet energy-saving goals. - Permit Fee Payment
Proof of payment for the solar permit fee, which varies by jurisdiction and the size of the installation. The fee typically covers the cost of processing the permit application and conducting necessary inspections. - Photographs of the Property
Photographs of the property, specifically the roof area where the panels will be installed. These images help inspectors assess the condition of the roof and identify any potential challenges or obstructions that might impact installation. - Inspection Requirements
A summary of inspection requirements, including scheduling information and what will be inspected (e.g., roof integrity, wiring, panel installation). The applicant may need to provide additional documents or access to certain areas of the property for inspection.
These documents ensure that the solar system will be safely and properly integrated into the building’s structure and electrical system, and help expedite the permitting process. The exact requirements can vary depending on the local jurisdiction, so it’s important to check with the local permitting authority for specific instructions.
Costs Associated with Solar Permitting
The cost of obtaining a solar permit in California can vary greatly depending on the size and complexity of the installation. For residential solar projects, permit costs generally range from $100 to $500 but can exceed this for larger systems or projects that require additional permits or inspections. Commercial solar installations often face higher permitting costs due to the complexity and scale of the projects. Additional fees may be charged for plan reviews, inspections, and electrical interconnections. Furthermore, jurisdictions may charge different fees depending on the location and the local cost of living. For instance, more affluent or urban areas may have higher fees. It’s also important to account for potential fees related to energy storage or battery systems, as these may require additional permits and inspections. Homeowners should budget for these costs when planning their solar installation to avoid any surprises. In some cases, fee waivers or reductions are available for low-income families or nonprofit organizations.
California Solar Permitting Fees
Solar permitting fees in California are determined by local jurisdictions, which vary in cost based on factors such as the scope of the project and location. For smaller residential installations, permitting fees typically range from $200 to $600. Larger commercial systems or those requiring additional infrastructure, such as energy storage, can incur higher fees. The permit cost is usually composed of several components: the building permit fee, the electrical permit fee, and other fees related to inspections or administrative processes. Certain cities or counties may also charge for plan review, which is an additional cost homeowners must account for. Additionally, utility companies may charge fees for interconnection to the grid, which can add to the overall cost of installation. California residents can check with their local permitting authorities to get a breakdown of the exact costs for their area. Some jurisdictions also offer fee reductions or waivers for low-income residents to promote solar energy adoption in underserved communities.
Inspection Requirements Post-Installation
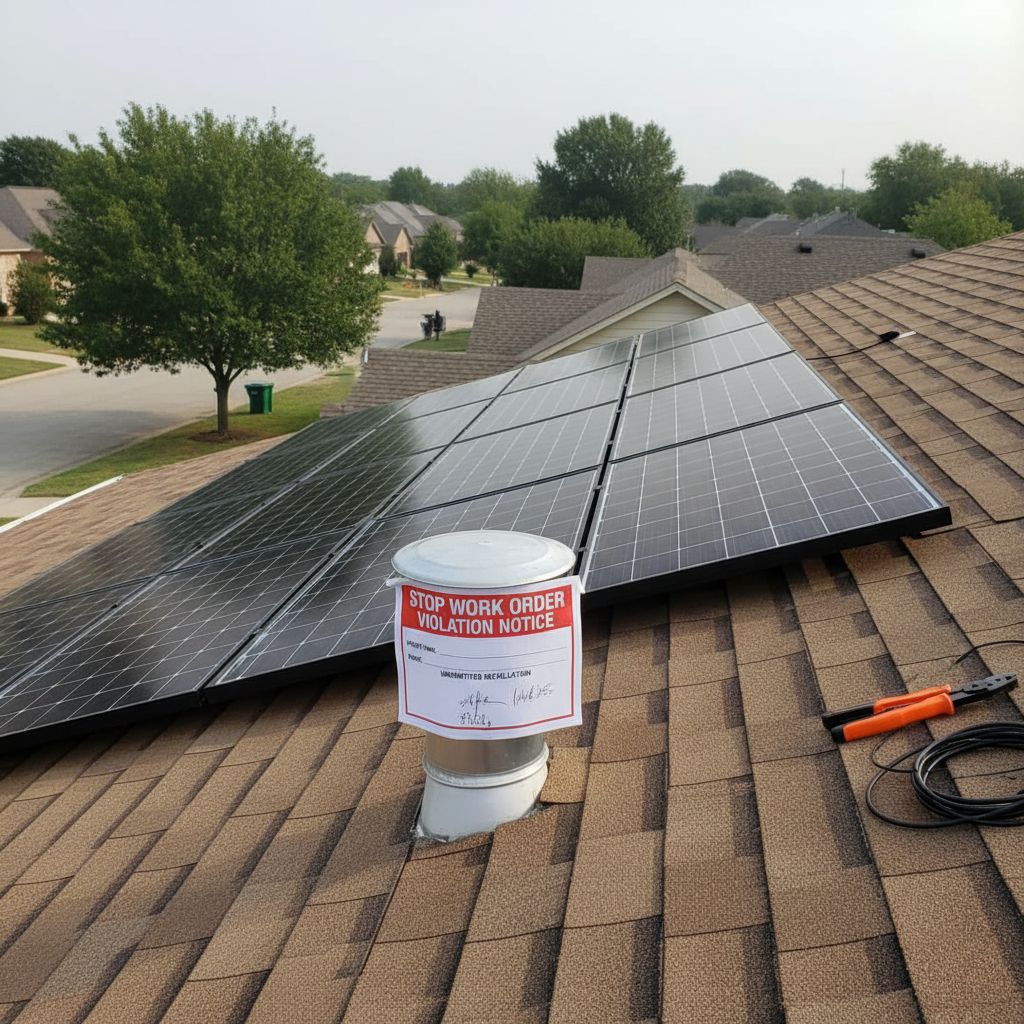
After the solar system is installed, it must undergo an inspection to ensure it meets safety and regulatory standards. Inspectors assess the system’s electrical connections, structural integrity, and overall safety. The inspection ensures that the system complies with local building codes and follows the approved plans submitted for the permit. If any issues are found, such as improper wiring or a lack of necessary safety features, the inspector may require the installer to correct the problem before re-inspection. After passing the inspection, the solar system is typically authorized for grid connection and can begin producing energy. In some cases, if a significant issue is identified, the system may fail inspection, requiring further work or modifications before approval. Post-installation inspections are crucial for confirming the solar system is operating correctly and safely, ensuring the protection of both property and people.
Net Metering and Utility Interconnection
In California, Net Energy Metering (NEM) allows homeowners and businesses with solar systems to receive credits for surplus electricity that is sent back to the grid. This process helps solar users offset the costs of their electricity consumption. To take advantage of net metering, however, homeowners must undergo a utility interconnection process, which involves applying for permission from the local utility to connect the solar system to the grid. The utility checks the system’s specifications to ensure it meets technical standards and does not pose a risk to the grid. Interconnection is an important part of the permitting process because it allows the solar system to function as a source of renewable energy that contributes to the state’s overall power supply. Utility companies in California may charge an interconnection fee for processing applications, although these fees tend to be relatively low. It’s crucial for solar customers to understand both the costs and benefits of net metering to ensure a financially viable installation.
Permit Expiration and Renewals
Solar permits in California typically have a validity period ranging from 180 days to one year. If the project isn’t completed within the allotted time frame, the permit may expire. When a permit expires, the applicant must apply for a renewal or reissue. This may involve resubmitting updated plans or documentation. In cases where significant time has passed, a re-inspection of the site may be required to ensure that the installation still meets current codes and standards. The need for renewal can arise due to various reasons, such as delays in the construction schedule or project changes. Homeowners and contractors should keep track of permit expiration dates to avoid unnecessary complications. In some cases, extensions may be granted by local permitting authorities, but this process requires filing the appropriate paperwork. Staying proactive about the timeline and understanding the rules for expiration and renewal can help avoid interruptions in the installation process.
Permitting for Solar Storage and Battery Systems
As solar energy adoption increases, many homeowners and businesses are opting to add solar battery storage systems to store excess power for later use. In California, these systems often require separate permits due to their complexity and the need to meet specific safety standards. Battery storage systems are governed by both electrical and fire safety codes, which ensure the systems are installed correctly and safely. Local jurisdictions often have specific guidelines regarding battery systems, which can vary by area. Some regions with high wildfire risks may impose additional requirements for fire-resistant materials and spacing between solar batteries. The process for obtaining permits for solar storage typically involves submitting a separate application detailing the battery type, capacity, and installation method. Local authorities may also require inspections after the system is installed to ensure compliance with safety regulations. With the increasing integration of energy storage into solar projects, it is important to understand the permitting process for these systems to avoid delays.
Challenges in Solar Permitting
While California has made significant progress in promoting solar energy, the permitting process can still be fraught with challenges. One of the most common issues is the complexity and inconsistency of local regulations. Each city or county may have slightly different requirements, which can make it difficult for homeowners or businesses to navigate the system. In some areas, long wait times for permit approval due to bureaucratic backlogs can delay solar installations. For larger commercial projects, the permitting process can become even more complicated, requiring extensive documentation, detailed plans, and multiple inspections. Furthermore, challenges with utility interconnection and compliance with safety regulations can also create delays. Finally, the cost of obtaining permits, particularly for projects involving energy storage, can become prohibitively expensive for some homeowners. Despite these challenges, California remains a leader in solar energy adoption due to its commitment to reducing barriers and promoting solar power as a clean energy solution.
Streamlining the Permitting Process
To encourage more widespread adoption of solar energy, California has taken several steps to streamline the permitting process. One notable development is the adoption of expedited permitting procedures for small residential systems, which has cut down approval times and made it easier for homeowners to get started with solar installations. In many jurisdictions, the California Solar Permitting Guidebook provides standardized procedures for cities and counties, ensuring that permitting processes are consistent across the state. The implementation of online permitting platforms has also made it easier for residents to submit applications and track the progress of their permits. These changes have helped reduce delays and simplified the paperwork required for solar projects. Furthermore, state-level initiatives, such as the SB 700 (2017) law, have mandated easier permitting for certain small-scale systems, including those with battery storage. By continuing to innovate and streamline procedures, California hopes to make solar power more accessible to everyone.
While the solar permitting process in California can be complex, it plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety, compliance, and efficiency of solar energy systems. Without proper permitting, solar systems might not meet building codes or electrical safety standards, posing risks to property owners and the wider community.
By adhering to the permitting process, California ensures that solar energy systems are installed correctly and safely, aligning with the state’s renewable energy goals. The state’s continuous efforts to streamline permitting procedures will make solar power more accessible and affordable, helping homeowners, businesses, and the environment benefit from this clean energy source. Despite the challenges, navigating the permitting process remains a vital step for anyone wishing to contribute to California’s renewable energy future.
Frequently asked questions
What is California solar permitting?
California solar permitting is the process of obtaining official approval from local building departments to install a solar energy system. It ensures that the installation complies with safety regulations, building codes, and energy efficiency standards required by state and local laws. Permits are needed for both residential and commercial solar installations to ensure proper installation and safe integration with the electrical grid.
Why do I need a permit for solar installation in California?
A permit is required to ensure that the solar installation meets all local building and safety codes. This includes verifying that the system is structurally sound, safely integrated into the electrical grid, and compliant with California’s energy efficiency standards. Without a permit, the installation could be unsafe, illegal, or fail to meet the necessary standards for utility connections.
How long does it take to get a solar permit in California?
The timeline for obtaining a solar permit in California can vary depending on the complexity of the project and the local jurisdiction. For residential installations, permits typically take one to two weeks to process. Larger, more complex installations may take longer, especially if additional documentation or reviews are needed.
What documents are needed to apply for a solar permit in California?
The documents required for a solar permit in California generally include a completed permit application, site and roof plans, electrical system diagrams, structural engineering reports, energy compliance forms, and manufacturer specifications for the solar panels and inverters. Depending on the location, additional documentation, such as photos of the property and proof of permit fee payment, may be required.
How much does a solar permit cost in California?
The cost of a solar permit in California varies based on the location and the size of the installation. Residential permits usually cost between $100 and $500, while commercial solar installations can cost more. Permit fees cover the administrative costs of reviewing applications and conducting inspections.
Can I install solar panels in California without a permit?
No, installing solar panels in California without a permit is illegal and could lead to penalties or fines. The permit ensures that the system is safe, meets all local codes, and is properly integrated into the building’s electrical system. Failure to obtain a permit could also result in the removal of the system.
What happens if my solar installation fails inspection in California?
If your solar installation fails inspection, the inspector will identify the issues that need to be corrected. These may include problems with wiring, structural support, or compliance with energy efficiency standards. After making the necessary adjustments, you can request a re-inspection. If the system passes, it will be approved for activation.
What are the benefits of obtaining a solar permit in California?
Obtaining a solar permit ensures that your installation is safe, legal, and compliant with local building codes. It helps prevent costly issues such as wiring errors, roof damage, or utility disconnections. It also enables access to available incentives and rebates, which can significantly reduce the overall cost of the system.
Can I install solar panels myself in California?
While it is possible to install solar panels yourself in California, it is recommended to hire a licensed contractor. Contractors are familiar with the permitting process, local codes, and safety requirements. DIY installations may face difficulties with permitting, inspections, and ensuring compliance with all applicable regulations.
Are there incentives for installing solar panels in California?
Yes, California offers several financial incentives for solar installations, including the federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC), the California Solar Initiative (CSI), and local rebate programs. These incentives can significantly reduce the upfront cost of installing solar systems, making it more affordable for residents and businesses to switch to solar energy.